 Mouse brain lipid segmentation using MALDI-MSI
Mouse brain lipid segmentation using MALDI-MSI
The Lipidomics Architecture of the Mouse Brain
Abstract
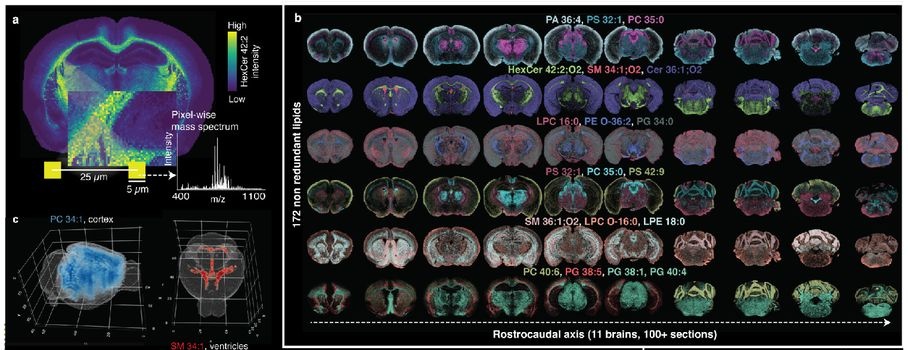
We present the first comprehensive lipidomic atlas of the adult mouse brain. Using high-resolution MALDI mass spectrometry imaging, we mapped 172 membrane lipids across 109 sections and 11 brains, registered to the Allen Brain Atlas. We identified 539 spatially coherent biochemical domains, or lipizones, representing fundamental units of lipid composition. Lipizones capture both neuronal bodies and distal terminals. While correlating with cell-type composition, lipizones are not reducible to the transcriptome by trivial regulation of enzyme expression; instead, they expose a new biochemical dimension of brain organization. The atlas revealed marked regional heterogeneity in white matter, driven by oligodendrocyte-specific lipids, and metabolic zonation in the ventricular system. Using the atlas, we discovered that pregnancy induces coordinated lipid remodeling in the cortex and white matter, marked by sphingolipid enrichment. This provides the first spatial framework to study lipid diversity in the brain and establishes lipids as an important axis of molecular architecture.